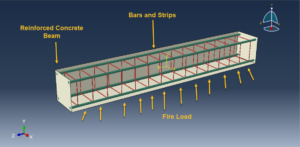
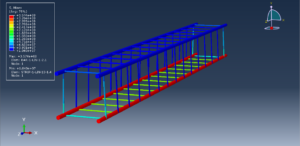
In this tutorial, the Simulation of RC Beams during Fire Events Using a Fully Coupled thermal stress Analysis in Abaqus has been studied. The concrete beam is modeled as a three-dimensional solid part. The steel reinforcements are modeled as wire parts. You can see a figure of the assembled parts below
The main concern relating to fire events is their classification (moderate or severe) and the evaluation of their impact on the structures. The classification of the fire assists in determining whether the structure is reusable or not after the extinguishment of the fire. The reason for the complexity of estimated residual structural capacity is its dependency on an enormous number of factors, such as mechanical pre-load during the fire, peak fire temperature, fire duration, degradation of thermal and mechanical properties of concrete and reinforcement, and boundary conditions of the structure, besides knowing the fact that not all material properties are reversible or valid during the heating, cooling, and post-fire loading stages. Research efforts to achieve structural safety and evaluate structural performance have been in demand recently due to the high capital investment in buildings and infrastructure sectors. The residual capacity for any structural element can be determined through destructive tests and non-destructive approaches
This tutorial mainly emphasizes the direct coupling technique (DCT), coupled elements, and how to apply it to fire events to fill the existing gap in the literature regarding DCT. As previously mentioned, most numerical simulations for structural elements under different fire scenarios implement either the sequential coupling technique (SCT) or simplified 2D models. This paper aims to study RC beams under fire conditions using DCT, and the same concept can be replicated with other research software packages such as ANSYS
The proposed methodology was based on a detailed numerical finite element model developed with the ABAQUS program, and DCT was chosen to join the thermal and structural analysis. Generally, two types of coupling techniques are available to connect thermal and structural analyses: SCT or DCT. SCT is based on running a thermal analysis and implementing these results into a structural analysis. On the other hand, for DCT, one model can perform thermal and structural analysis, as coupled elements can express both the thermal and the structural degrees of freedom. Convection loads are used to apply fire loads on different areas for the beam with film coefficients to simulate the desired fire scenario and determine the surfaces in direct contact with the fire. The convection loads vary with time according to the applied fire curve. The proper mesh and boundary conditions are assigned to all parts
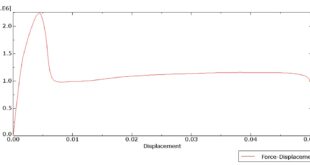
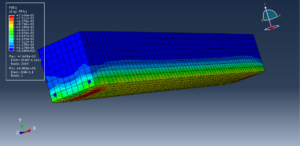
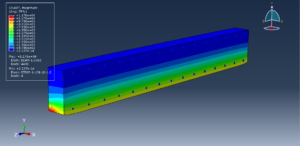
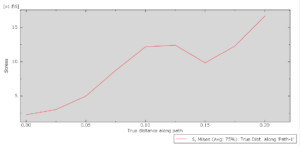
After the simulation, all results like stress, temperature, heat flux, strain, displacement, and so on are available. You can see some figures for the results below
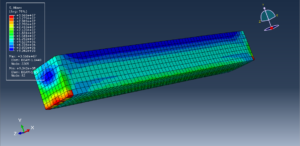
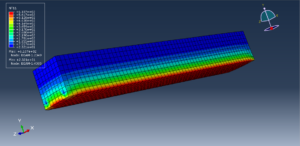
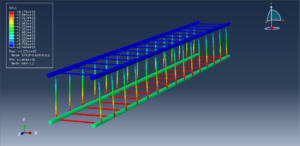
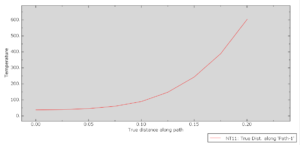
You can provide CAE, INP, and English video files of this simulation here. The cost of these files is Thirty Euros. you can click on the bellow bottom to begin the process
You can purchase the tutorial through a PayPal account, a Visa, or a Master card, just before payment, send me an email to this address: karampourp@gmail.com
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials