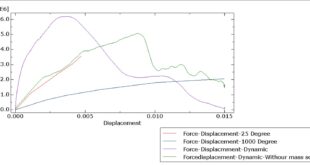
Introduction to Simulation of Blast Resistance Behavior of Adhesively Bonded Cross-Laminated Timber-Concrete Composite (CLT-CC)
Overview
The simulation of blast resistance behavior in adhesively bonded cross-laminated timber-concrete composites (CLT-CC) represents an emerging area of research in structural engineering and blast mitigation. This composite system combines the advantages of cross-laminated timber (CLT) and concrete to create hybrid structures with improved performance under extreme loading conditions
Composite System Characteristics
CLT-CC systems typically consist of
Cross-laminated timber panels (3-7 layers of orthogonally arranged wood boards)
Concrete topping layer (usually 50-150mm thick)
High-performance adhesive interface bonding the two materials
Blast Resistance Considerations
The blast resistance of CLT-CC composites depends on
Material properties: Timber’s energy absorption capacity and concrete’s compressive strength
Composite action: Effective stress transfer through the adhesive layer
Failure modes: Delamination, timber fracture, and concrete crushing
Dynamic response: Strain rate effects on material behavior
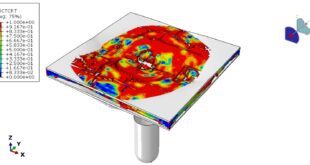
You can see a figure of the assembled part in Abaqus below
Key Simulation Challenges
Accurate modeling of rate-dependent material properties
Representation of complex adhesive interface behavior under dynamic loading
Computational efficiency for large-scale simulations
Applications
Understanding blast resistance through simulation enables
Design of more resilient hybrid structures
Retrofit solutions for existing buildings
Development of performance-based design guidelines
Optimization of material combinations and thicknesses
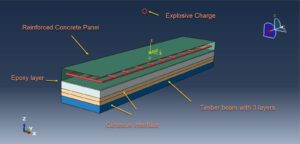
In this example, the epoxy is used as the interface between the concrete and the first wood layer, and cohesive interaction is used between the wood layers. The CONWEP air blast model is selected. CONWEP (Conventional Weapons Effects Program) is an empirical blast load model developed by the U.S. Army and implemented in ABAQUS (via the Explosive Load or Blast Load option) to simulate airblast effects from high explosives. It is based on experimental data and provides a simplified yet efficient way to model blast pressure waves without explicitly modeling the explosive detonation or fluid-structure interaction (FSI)
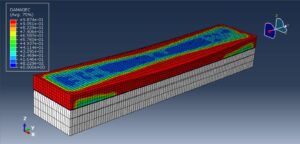
After the simulation, all results such as stress, strain, failure, damage, wood failure, compression and tension damage, cohesive interaction failure, and others are available. You can see some figures of the results below
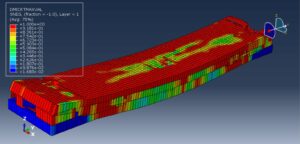
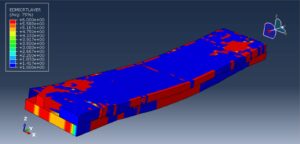
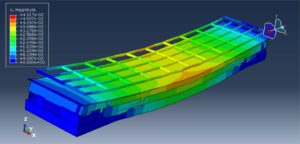
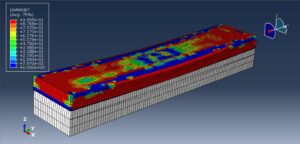
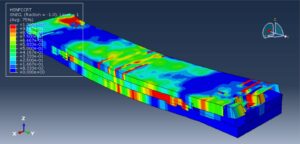
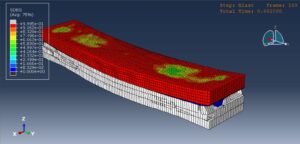
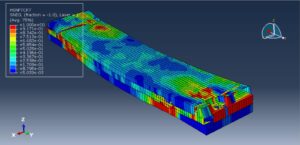
You can provide this simulation’s CAE, INP, and English video files here. The price of these files is Twenty-Six Euros. You can click on the button below to begin the process
Our Payment methods are: Tether, Bitcoin, TRX, PayPal, Visa, or Mastercard. Just before payment, send us an email to this address: abaqusfem.com@gmail.com
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials