Fire behavior of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) composites has been extensively studied due to their increasing use in aerospace, automotive, and civil engineering structures, where fire safety is critical. The literature consistently highlights that CFRP exhibits excellent mechanical performance at ambient conditions but suffers significant degradation when exposed to elevated temperatures or direct flame
Thermal Degradation and Material Behavior
Research shows that the polymer matrix is the primary source of vulnerability in fire
Glass transition (Tg) and resin softening occur at relatively low temperatures (80–۲۰۰°C)
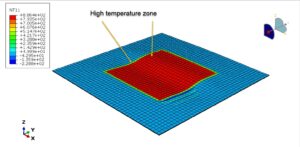
Above ≈۳۰۰°C, resins begin pyrolysis, producing volatiles, smoke, and char
Carbon fibers maintain structural integrity up to ≈۶۰۰–۷۰۰°C but may undergo oxidation in an oxygen-rich fire environment
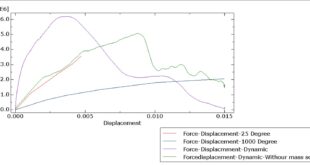
Studies using TGA, DSC, and DMA quantify mass loss and shifts in mechanical performance, revealing a strong correlation between temperature exposure and stiffness/strength reduction
Structural Response Under Fire
Experimental work (e.g., cone calorimetry, burner tests) shows
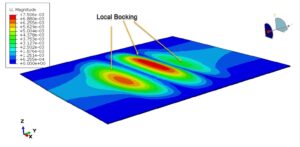
Early interlaminar delamination caused by thermal expansion mismatch
Matrix recession and char formation, reducing load-bearing capacity
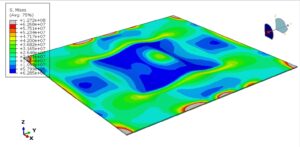
Residual strength degradation after fire exposure is significant, even if temperatures do not reach fiber oxidation levels
Fire Modeling Approaches
Thermal Modeling
Transient heat conduction, Convective and radiative boundary conditions, and Temperature-dependent thermal properties
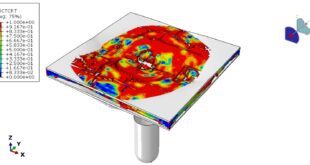
Thermo-Mechanical Coupled Analysis
Temperature-dependent elastic moduli and strengths, Stiffness degradation laws based on Tg, resin pyrolysis, or empirical reduction curves, and Progressive failure criteria (e.g., Hashin, Puck, Chang–Chang) if it would be available
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) composites are increasingly used in aerospace, automotive, marine, and civil engineering structures due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and excellent fatigue performance. However, their behavior under fire exposure is a critical design concern, as CFRP materials differ significantly from metals in thermal response and degradation mechanisms.
Fire analysis of CFRP composites focuses on understanding how elevated temperatures, combustion products, and heat flux affect both the polymer matrix and the carbon fibers
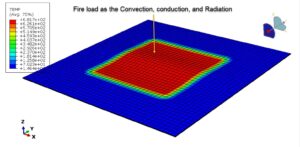
During this course, you’ll learn all about the fire analysis of CFRP composite materials through a practical and comprehensive tutorial. Topics include solid geometry definition for CFRP, temperature-dependent material modeling, fully coupled analysis, fire definition using convection, conduction, and radiation, meshing, and results analysis.
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials