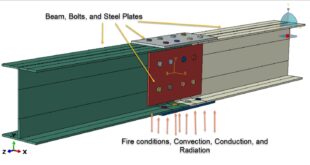
In this example, the RT-PMMA is modeled as a three-dimensional solid part, while the CFRP composite material is modeled as a shell part. To represent the RT-PMMA behavior under high-velocity impact, the elastic–extended Drucker–Prager plasticity model and a ductile damage formulation are used. Hashin’s damage criterion is applied to the CFRP fibers. An explicit analysis step and general contact capability are included in the input file to account for the full failure behavior
Rubber-toughened poly(methyl methacrylate) (RT-PMMA) reinforced with carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) is an advanced hybrid material system designed to combine the optical clarity, lightweight characteristics, and strain-rate sensitivity of PMMA with the high specific strength and stiffness of carbon-fiber composites. Such hybrids have growing relevance in engineering applications that demand excellent impact resistance—such as transparent armor systems, aircraft canopies, automotive glazing, and protective structural components—where maintaining structural integrity under high-velocity projectile impact is essential
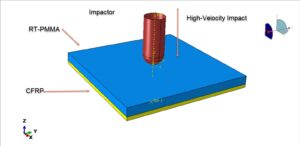
High-velocity impact simulation of RT-PMMA/CFRP systems presents distinctive modeling challenges due to the coexistence of multiple deformation and failure mechanisms. RT-PMMA exhibits nonlinear viscoelastic–viscoplastic behavior, shear yielding, and cavitation-based toughening arising from dispersed rubber particles. Under ballistic-scale strain rates, its strength and energy-absorption capacity can increase significantly, making accurate constitutive modeling crucial. CFRP, by contrast, is highly anisotropic and brittle, with failure dominated by fiber breakage, matrix cracking, and interlaminar delamination. When bonded together, the hybrid laminate undergoes complex stress wave interactions, interfacial debonding, and progressive damage evolution that strongly influence penetration resistance and residual velocity
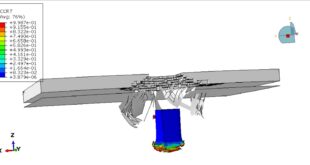
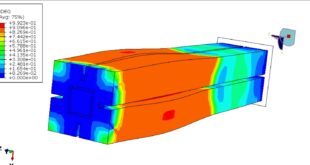
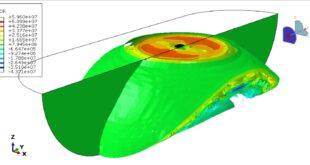
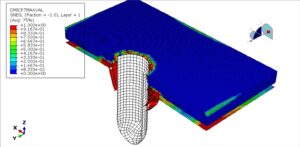
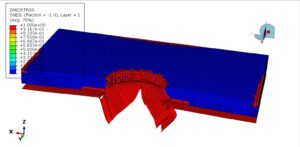
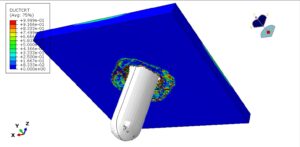
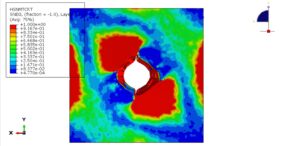
After the analysis, all results, such as stress, strain, damage, failure, penetration, and …, are available. You can see some figures of the results below
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials