Introduction to Timber Wood Beam Reinforced with GFRP Rod and Epoxy Interface under Bending Test
Overview
The reinforcement of timber wood beams using Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) rods with an epoxy interface represents an innovative approach to enhancing the structural performance of traditional timber elements. This composite system combines the natural advantages of wood with the high tensile strength and corrosion resistance of GFRP materials
Background
Timber has been a fundamental construction material for centuries due to its
Renewable nature
Favorable strength-to-weight ratio
Aesthetic qualities
Thermal insulation properties
However, timber suffers from several limitations: Anisotropic behavior (strength varies with grain direction), Susceptibility to moisture and biological degradation, and Variable mechanical properties. Limited tensile strength perpendicular to the grain
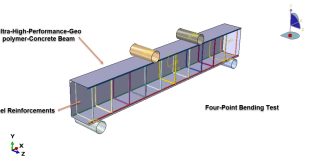
You can see a figure of the assembled parts below
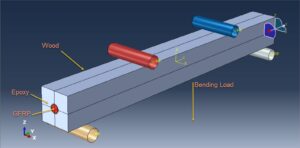
Components of the System
Timber Beam: The primary load-bearing element, typically softwood or hardwood, with known mechanical properties
GFRP Rods: High-strength fiber-reinforced polymer rods that provide tensile reinforcement
Epoxy Interface: The adhesive layer that ensures effective stress transfer between the timber and GFRP components
Purpose of Bending Tests
Bending tests are conducted to evaluate
Load-bearing capacity improvement compared to unreinforced timber
Failure modes and mechanisms
Stiffness enhancement
Ductility characteristics
Effectiveness of the epoxy bond interface
Key Research Focus Areas
Composite Action: How effectively the GFRP and timber work together
Failure Modes: Whether failure occurs in timber, GFRP, or at the interface
Load-Deflection Behavior: Stiffness characteristics under increasing load
Long-Term Performance: Though accelerated tests may be needed
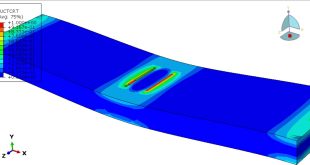
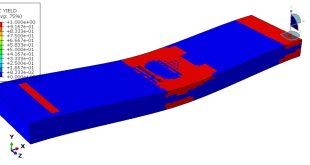
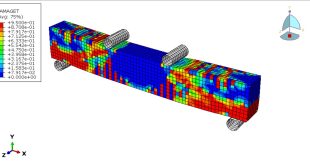
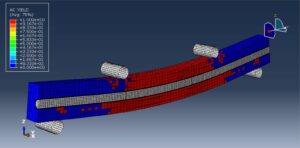
The four-point bending test is performed using the general static step. All results stress, strain, damage, failure, force-displacement, and others, are available. You can see some figures of the results below
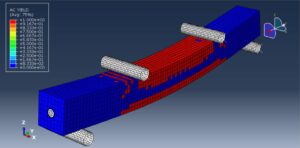
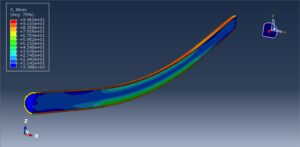
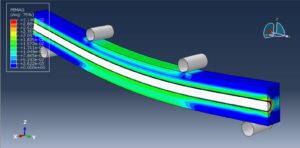
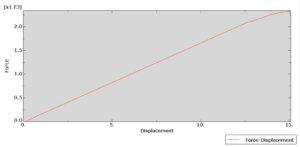
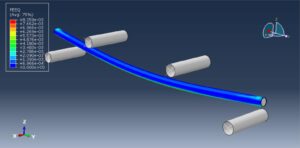
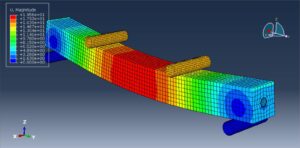
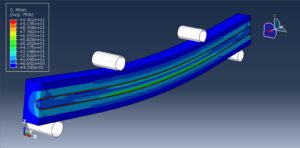
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials